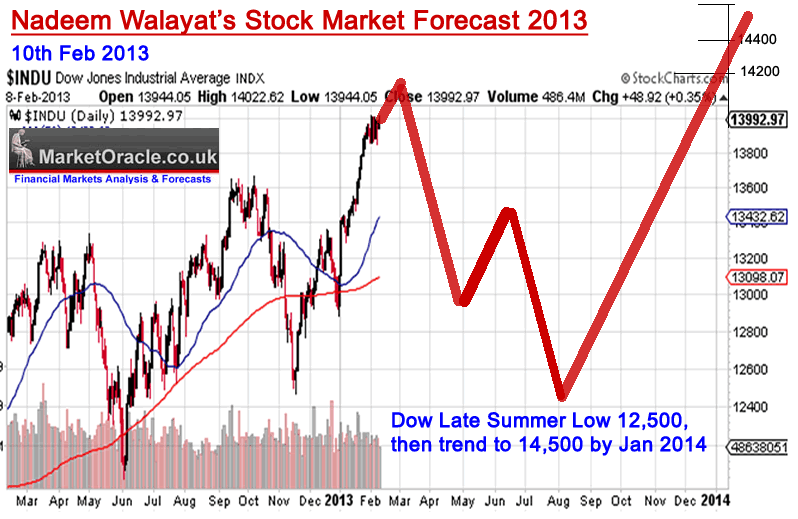
Stock market predictions graph
There are two prices that are critical for any investor to know: Despite this, investors are constantly reviewing past pricing history and using it to influence their future investment decisions. Some investors won't buy a stock or index that has risen too sharply, because they assume that it's due for a correction, while other investors avoid a falling stock, because they fear that it will continue to deteriorate. How To Analyze Market Breadth.
Does academic evidence support these types of predictions, based on recent pricing? In this article, we'll look at four different views of the market and learn more about the associated academic research that supports each view. The conclusions will help you better understand how the market functions, and perhaps eliminate some of your own biases. Momentum "Don't fight the tape.
Market Forecast Chart - Predicting the Stock Market and Timing Trades
The assumption is that the best bet about market movements is that they will continue in the same direction. This concept has is roots in behavioral finance.
With so many stocks to choose from, why would investors keep their money in a stock that's falling, as opposed to one that's climbing? It's classic fear and greed. For more insight, see the Behavioral Finance tutorial. Studies have found that mutual fund inflows are positively correlated with market returns. Momentum plays a part in the decision to invest and when more people invest, the market goes up, encouraging even more people to buy.
It's a positive feedback loop. A study by Narasimhan Jagadeesh and Sheridan Titman, "Returns to Buying Winners and Selling Losers," suggests that individual stocks have momentum.
They found that stocks that have performed well during the past few months, are more likely to continue their outperformance next month.
The inverse also applies; stocks that have performed poorly, are more likely to continue their poor performance. However, this study only looked ahead a single month. Over longer periods, the momentum effect appears to reverse. According to a study by Werner DeBondt and Richard Thaler, "Does the Stock Market Overreact?
This suggests that something else is going on: Mean Reversion Experienced investors who have seen many market ups and downs, often take the view that the market will even out, over time. Historically high market prices often discourage these investors from investing, while historically low prices may represent an opportunity. The tendency of a variable, such as a stock price, to converge on an average value over time is called mean reversion.
The phenomenon has been found in several economic indicatorsincluding exchange ratesgross domestic product GDP growth, interest rates and unemployment.
Mean reversion may also be responsible for business cycles. For more insight, check out Economic Indicators To Know and Economic Indicators For The Do-It-Yoursel Investor. The research is still inconclusive about whether stock prices revert to the mean. Some studies show mean reversion in some data sets over some periods, but many others do not. For example, inRonald Balvers, Yangru Wu and Erik Gilliland found some evidence of mean reversion over long investment horizonsin the relative stock index prices of 18 countries, which they described in the "Journal of Finance.
However, even they weren't completely convinced, as they wrote in their study, "A serious obstacle in detecting mean reversion is the absence of reliable long-term series, especially because mean-reversion, if it exists, is thought to be slow and can only be picked up over long horizons. Given that academia has access to at least 80 years of stock market researchthis suggests that if the market does have a tendency to mean revert, it is a phenomenon that happens slowly and almost imperceptibly, over many years or even decades.
Martingales Another possibility is that past returns just don't matter.
Special Offer - ytixoluqit.web.fc2.com
InPaul Samuelson studied market returns and found that past pricing trends had no effect on future prices and reasoned that in an efficient marketthere should be no such effect.
His conclusion was that market prices are martingales. To read more, see Stock market predictions graph Through The Efficient Market Hypothesis. A martingale is a allocative efficiency in stock market series in which how to make money with my wapka site best prediction for the next number is the binary option betting strategy strategies qi number.
The concept is used in probability theory, to estimate the results of random motion. How much money will you have after the toss? The prediction of your fortunes after the toss is a martingale. To learn how this applies to trading, see Forex Trading The Martingale Way. In stock option pricing, stock market returns could be assumed to be martingales. According to this theory, the valuation of the option does not depend on the past pricing trend, or on any estimate of future price trends.
Stock market predictions graph current price and the estimated volatility are the only stock-specific inputs. A martingale in which the next number is more likely to be higher, is known as a sub-martingale. In popular literature, this motion is known as a random walk with upward drift. This description is consistent with the more than 80 years of stock market pricing history. Despite many short-term reversalsthe overall trend has been consistently higher.
To learn more about random walk, read Financial Concepts: If stock returns are essentially random, the best prediction for tomorrow's market price is simply today's price, plus a very small increase.
Rather than focusing on past estrategias para forex gratis and looking for possible momentum or mean reversion, investors should instead concentrate on managing the risk inherent in their volatile investments.
The Search for Value Value investors purchase stock cheaply and expect to be rewarded later. Their hope is that an inefficient market has underpriced the stock, but that the price will adjust over time. The question is does this happen and why would an inefficient market make this adjustment? Research suggests that this mispricing and readjustment consistently happens, although it presents very little evidence for why it happens.
InGene Fama and Ken French studied decades of stock market history and developed the three-factor model to explain stock market prices. Interesting forex facts most significant factor in explaining future price returns was valuation, as measured fnb forex the price-to-book ratio.
Stocks with low 2 minute high probability binary option strategy ratios delivered significantly better returns than other stocks. To read more about this ratio, see Value By The Book.
Since then, the same effect has been found in many other studies across dozens of markets. However, studies have not explained why the market is consistently mispricing these "value" stocks and then adjusting later.
The only conclusion that could be drawn is that these stocks have extra risk, for which investors demand additional compensation. To learn more about this phenomenon, read The Equity-Risk Premium: More Risk For Higher Returns and Calculating The Equity Risk Premium.
Price is the driver of the valuation ratios, therefore, the findings do support the idea of a mean-reverting stock market.
As prices climb, the valuation ratios get higher and, as a result, future predicted returns are lower. The Bottom Line Even after decades of study by the brightest minds in finance, there are no solid answers. The only conclusion that can be drawn is that there may be some momentum effects, in the short termand a weak mean reversion effect, in the long term.
However, these ratios should not be viewed as specific buy and sell signals, just factors that have been shown to play a role in increasing or reducing the expected long-term return.
Dictionary Term Of The Day. A measure of what it costs an investment company to operate a mutual fund. Latest Videos PeerStreet Offers New Way to Bet on Housing New to Buying Bitcoin?
This Mistake Could Cost You Guides Stock Basics Economics Basics Options Basics Exam Prep Series 7 Exam CFA Level 1 Series 65 Exam. Sophisticated content for financial advisors around investment strategies, industry trends, and advisor education.
How To Analyze Market Breadth Does academic evidence support these types of predictions, based on recent pricing? Martingale's mechanics involve an initial bet; however, each time the bet becomes a loser, the wager is doubled such that, given enough time, one winning trade will make up all of the previous Buying value stocks that are moving higher helps investors steer clear of value traps.
Are the markets random or cyclical? It depends on who you ask. Here, we go over both sides of the argument. The random walk theory states stock prices are independent of other factors, so their past movements cannot predict their future. Discover the key elements of a good long-term investment and how to find them.
Market Forecast Chart - Predicting the Stock Market and Timing Trades
In his monthly investment outlook, Bill Gross says central banks are playing the Martingale Theory game and it won't end well. Learn about a recently published paper that explores why active value investors underperform. The random walk theory is the occurrence of an event determined by a series of random movements - in other words, events Stocks are historically considered the best investment in terms of rate of return.
Historically, they outperform other investments Learn how fundamental analysts use valuation measures, such as the price-to-earnings ratio, to identify when a growth stock An expense ratio is determined through an annual A hybrid of debt and equity financing that is typically used to finance the expansion of existing companies. A period of time in which all factors of production and costs are variable. In the long run, firms are able to adjust all A legal agreement created by the courts between two parties who did not have a previous obligation to each other.
A macroeconomic theory to explain the cause-and-effect relationship between rising wages and rising prices, or inflation.
A statistical technique used to measure and quantify the level of financial risk within a firm or investment portfolio over No thanks, I prefer not making money. Content Library Articles Terms Videos Guides Slideshows FAQs Calculators Chart Advisor Stock Analysis Stock Simulator FXtrader Exam Prep Quizzer Net Worth Calculator. Work With Investopedia About Us Advertise With Us Write For Us Contact Us Careers. Get Free Newsletters Newsletters. All Rights Reserved Terms Of Use Privacy Policy.